- Mac Scan For Ip Addresses On Network Topology
- Scan For Ip Addresses On Network Cmd
- Scan Ip Addresses On Network Mac Terminal
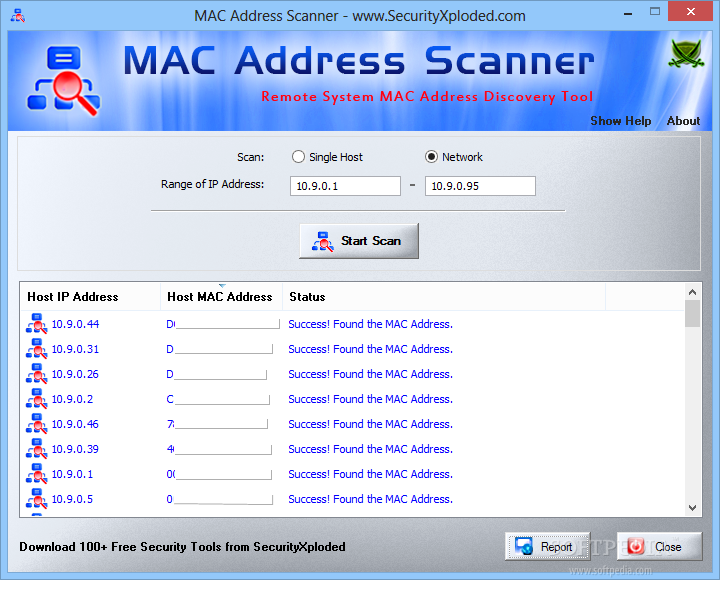
Download Colasoft MAC Scanner Colasoft MAC Scanner will send out ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) queries to the specified subnet and listen to the responses from all the hosts in the subnet, then list the MAC addresses and IP address in pairs.
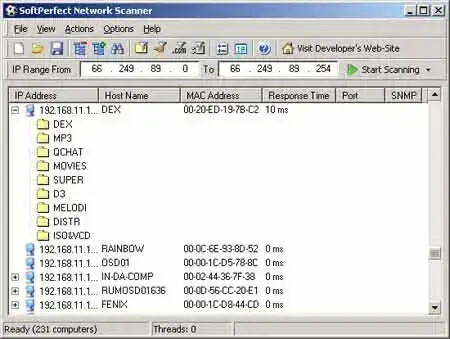
- IP-MAC Scanner is a powerful network solution that helps administrators scan the network and manage information on every single connected system. A well thought out GUI lets you perform a scan.
- A MAC address scanner scans the network for IP addresses and their associated MAC addresses. It enables users to scan hosts one at a time or a group of hosts at a time. MAC scanners allow users to find the IP and MAC addresses of devices accessing their network and to trace crucial client information like DNS engagement and hostnames.
- ARPmyNET is a network ip scanner which can scan all the known and unknown devices connected to your LAN network with their MAC Address. You can input the IP range by inputting and from plain text file. After scanning, it can save scanned data to plain text file.
Network scanning is a necessary task, but it can start off simple and rapidly become more complicated as your business gets larger. Manually finding IP addresses on your network is possible, but why do it yourself when there are so many tools to help you? Not only can network scanning tools help you find IP addresses, but they can also provide extra information for monitoring, troubleshooting, and keeping your network running efficiently.
My top choice for a network scanning tool is the SolarWinds® IP Address Manager, as it works in an intuitive and easy-to-use way while offering a broad suite of tools and functions. It’s more approachable than some of the other tools out there and has a flatter learning curve for figuring out how to get started.
How to Find IP Addresses of Devices on My Network
Curious how to find IP addresses on-network? You may need to know about either static or dynamic IP addresses. If you can access your router, you may be able to simply view the client lists and get information like hostname and MAC address. Or you can use a device connected to the network to ping the network and view the ARP tables. Done manually in this way, you have to do everything through the command line. Use the prompt “ipconfig” on Windows to get network settings, followed by “arp -a” to view IPs plus MAC addresses.
However, this method doesn’t work across subnets. This means that if you have multiple subnets on your network, you have to go through each individual router or subnet to determine the IP addresses within the subnet. It becomes pretty clear as your network scales, manually scanning for IP addresses becomes an extremely complex task. Multiple subnets and an ever-changing string of devices connecting to and disconnecting from the network becomes problematic.
Instead of attempting to manually manage these aspects of your network, I recommend using an IP address manager (IPAM). These tools help you to manage your IP addresses and troubleshoot problems, but they also help you to find all the IP addresses of the devices on your network and determine the status of each one (dynamic, static, available, reserved, etc.). Some tools will also integrate with DNS and DHCP, and all of them will usually present data in a visual, interactive format. Many also allow you to save your network scanning results and present them in spreadsheets or reports.
Best Network Scanner Tools 2020
SolarWinds IP Address Manager

This is my top choice for network scanning software. The SolarWinds IP Address Manager (IPAM) with its IP Address Scanner feature is great for both beginner users and small businesses, and expert network administrators and large enterprises. With automated IP address tracking and integrated DHCP and DNS management, you can quite easily monitor your IP addresses and associated network information.
You can also see all your subnets and how they are structured, and which subnets and scopes don’t have much free space remaining. It allows you to flag capacity issues before they become a problem so that IP address issues don’t affect performance. I’ve also found it’s easy to find unused IPs and reclaim them to tidy up my networks.
This IPAM uses a clean and simple interface, without a steep learning curve like some other IP address managers. You can easily assign management or control permissions to other admins or admin groups, allowing you to delegate tasks simply within the IPAM rather than needing to use another tool. The console is centralized, allowing you to see all the relevant information in one place, reducing the potential for error.
I consider the SolarWinds IPAM to be a complete solution, and it’s my choice for an all-round lightweight tool you can use to scan and maintain your network. There’s a free trial available so you can try it out, then level up to gain access to more features and greater scalability.
MyLanViewer
This is another strong business-level contender for network scanner tools. MyLanViewer is an IP and network scanner, as well as a traceroute tool and network monitor. It uses a buddy-list style window to display all of your network computers, including important technical information about each one. It can scan your network to monitor IPs and let you know when any details change. It also supports remote shutdown and other remote functions for each network computer. It can monitor hidden devices on your subnets and discover bottlenecks in your connection with its traceroute tool. I’d say this is a fine choice for business use—it has an easy-to-use interface and is suitable for beginners and advanced users.
Angry IP Scanner
Looking for one of the best free tools? This is an open-source and free network scanning tool, with the ability to scan ports and IP addresses quickly and efficiently. The tool provides a report of data on each device on the network, including NetBIOS, MAC and IP address, computer name, and hostname. Keep in mind that open-source tools do require a bit more know-how on the user’s part and aren’t my usual pick for business use.
Angry IP Scanner can also produce reports in XML, CSV, and TXT format, which is useful for exporting data and other things within your business. Its unique feature is it uses a multi-threaded scanning approach, which uses a separate scanning thread for each IP address. This helps to improve the scanning process and make it more accurate.
Picking the Best IP Scanner
When I want to discover IP addresses on my network or scan for data generally, I tend to lean toward using a network scanning tool rather than trying to do it manually. Many network scanners have simple interfaces, and some go above and beyond in terms of ease-of-use and clean interface appearance. I like using the SolarWinds IP Address Manager, as it contains a pretty hefty solution in a lightweight package, with a free trial for people who want to try it out without commitment.
Recommended Reading
Ultimate Guide to Network Monitoring: If you’re looking for more in-depth information on how to monitor and look after your network, take a look here for a beginner’s guide followed by more expert-level instructions.
Scanning for IP address lets you have better control over your network. With 1-2 commands, you can quickly map out the devices in your network and the IP addresses that they are using. But to understand how to scan a network, first, you need to understand how are IP addresses assigned.
DHCP (Assigning IPs Dynamically)
An automated process in networking, called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), assigns IP dynamic addresses to hosts as soon as they enter the network. In a home or small network, the DHCP server is usually a part of the router. When you come into the network, the router will look for an available IP address in its pool and assign it to you, so that your device can communicate with others without any conflict.
Dynamic allocation of IP addresses is a great advantage for both end-users and network admins. But sometimes you would need to have some control in order to manage and troubleshoot your network more efficiently.
What will you learn in this Tutorial
In this tutorial, you will learn the basic networking skills on how to scan a network for IP addresses. We will scan a network with native OS commands, find which addresses were assigned dynamically, which statically, and test their connectivity.
In the end, we will compare some IP address scanning tools that can give you additional information. To improve your IP addressing insights, even more, we will show you some tools that allow you to track IP addresses and even manage them.
Simple IP Scanning
Operating Systems, like Windows and Linux, come with their own native simple networking set of tools. Commands such as “ipconfig”, “arp -a”, or “ping” allow simple scanning and troubleshooting.
The simplest way to get a quick list of IP addresses and their devices connected to your network is with those OS native commands found in the command line. With a list of the assigned IP address and their devices, you can easily find the devices that are causing the most problems.
- ipconfig
This command displays all network settings assigned to one or all adapters in the computer. You can find information such as your own IP, subnet, and Gateway. For Linux and MacOS is “Ifconfig”. - arp -a
When you issue the “arp -a”, you’ll get IP-address-to-mac conversion and the allocation type (whether dynamic or static) of all devices in your network. - Ping
It helps determine connectivity between two hosts and find the IP address of a hostname.
- ipconfig
Reading The Output
Finding your own network adapter configuration
In the following screenshot, you’ll see the output from the ipconfig command. On a Windows, the ipconfig command can be entered through the Command line.
Go to Run > type cmd > type ipconfig
- This Windows computer has 5 network adapters, but the last one (Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi) is the only one connected to a network. The rest are disconnected.
- In this network, the router (or Default Gateway) is playing the role of the DHCP server. It is assigning the IP address dynamically and giving access to the Internet.
- You are reading two of the most important IP addresses for your device; Your own device’s IP (IPv4 and IPv6) and your Gateway. The Subnet Mask is also very important, it shows that you are on the same subnet as the gateway.
Now you know your subnet, which in this case is 192.168.1.0/24 (using the CIDR range). Now you need to find the rest of the IP address in your network.
Scanning your Network
The job of the ARP protocol is to map IPs to MAC addresses. It provides a method for hosts on a LAN to communicate without knowing any address and create a cache of information. When a new computer enters the LAN, it receives an IP and updates its ARP cache with the Gateway information. This ARP cache can be found using the “arp-a” command.
- Use the command line to enter the “arp -a” command.
- This computer has been connected for some time into the LAN, so its ARP cache is very precise and complete. The first IP address shown in the display is the Gateway (the same we found through the ipconfig command).
- The output shows the IP, the MAC addresses, and their assignation type. The addresses displayed here were dynamically assigned by the DHCP server in the LAN. All of these IPs are devices connected to the LAN (192.168.1.0/24). The other static addresses are reserved for Multicasting.
- With the MAC information, you can know the vendor. Try searching for vendor prefixes or use an automatic online tool such as MACvendors.
Testing Connectivity
Finally, with some information, you can test connectivity. In the following test, we tried an extended ping with “ping -t” to the gateway. With this, you can learn some simple insights about delay and latency.
From the list generated by the ARP command, you could ping all the live hosts. Or you can go beyond and ping the entire subnet to find hosts not found by the ARP (but that would be too much manual work…). Later, we’ll discuss how to automatically ping entire subnets at once.
Although having a list of devices and their allocated IP address will give you good insights, the information will not be enough when your network scales. Manual IP scanning in multiple subnets and BYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Device) scenarios is nearly impossible. As the network scales, problems will scale too.
Larger networks demand more results, flexibility, and easy-to-read set of commands.
An IP Address Scanner tool helps you with larger demands. These tools are able to map the entire local network, finds live hosts, and to provide the results of the “arp-a” in a clearer format. Other IP Scanners do not depend on ARP but they operate using repeated ping tests. A Ping Sweep tool lets you ping entire subnets and find live hosts just with one button.
Some other IP Scanners go the extra mile and give more information such as Port number, DNS, DHCP, etc. All of this data is also presented in the most visual and easy-to-read format. They also allow users to save all results and present them in detailed reports.
Advanced IP Scanners
1. Angry IP Scanner
Angry IP Scanner is one of the most popular scanners on the web, with over 29 million downloads. It is open-source, free, and available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux. It can let you scan your local network or the Internet-facing IP addresses.
This tool is not only capable of scanning IP addresses but also ports. When you define an IP address range, you can also specify a number of the port, and see if a device in your network is using a specific service (defined by the port). Angry IP Scanner also lets you save all the scan results into multiple formats, such as TXT, XML, CVS, etc.
When you scan, you’ll know what hosts are alive, their response time, hostname, MAC address, etc. If you want even more information, you can extend results by developing Java plugins.
Price:
Open Source and 100% free.
Download:
Get Angry IP from its official site.
2. SolarWinds Ping Sweep
Ping Sweep from SolarWinds helps you find free IPs and identify which ones are unavailable. It is classified as a networking discovery tool from the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset. A comprehensive network software, that includes over 60 handy tools. Ping Sweep from SolarWinds is included in the Engineer’s Toolset and is dedicated for ping testing. For the MAC address, port scans, SNMP scans, etc, there are more dedicated tools in the Engineer’s Toolset.
Just as when you ping from the command line, this tool shows the DNS name for each IP and response time. It can also let you export results in different formats such as CSV, TXT, XLS, and to an HTML page.
Price:
SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset starts at $1,380.00 and includes over 60 must-have tools.
Download:
Get a fully functional Engineer’s Toolset for 14 days by registering to SolarWinds official site.
IP Address Tracker Tools
Having a map of IP addresses, MAC addresses, used ports, etc, is great for networking inventorying and may help with some troubleshooting cases. But a list can not control and display real-time results.

An IP address Tracker is a good upgrade to our set of tools and commands described so far. It does allow scanning multiple subnets and displaying results, but it also allows you to keep track of one or more IP addresses.
An IP Address Tracker will notice when an IP address is released. This can be either because the device lost connectivity or it changed IP address. It will help you minimize IP addressing conflicts (when two devices are trying to take the same IP) and reduce DNS errors.
3. MyLAN Viewer
MyLAN Viewer is a NetBIOS and IP address scanner for Windows systems. Just like the IP Scanners shown above, this tool will scan a network and show devices in an easy-to-read format.
But MyLANViewer goes beyond, and not only shows computer name, IP, and MAC, but also NIC, OS version, logged users, shared folders, and much more.
This tool is able to track specific IP addresses and show notifications when their state change. With it, you can also keep track of network security by showing port information and detecting rogue DHCP servers. MyLAN Viewer tracks all devices in the subnet including hidden, and displays alerts when new devices enter the network, and others go.
This tool can also display the following metrics as well:
- Display Whois data.
- Perform traceroute.
- Manage “Remote Shutdown and Wake On LAN (WOL)”.
- Monitor wireless networks.
Price:
Free, but only available for Windows systems.
Download:
Get MyLAN Viewer from its official site.
4. SolarWinds IP Tracker
SolarWinds IP Tracker is a standalone software and completely free. In addition to creating inventories of all devices, this tool allows you to scan, track, and manage IP address, including their event logs, all in a single place. SolarWinds IP Tracker is the free version and feature-limited of the much coveted IP Address Manager.
But the IP Tracker does an amazing job to provide a centralized view of the entire IP addressing scheme. It lets you monitor 256 (one subnet) IP addresses for free. Additionally, this tool allows basic management functionalities with tools such as, Ping, Telnet, Traceroute. The best of all is that, with SolarWinds IP Tracker you can detect IP address conflicts created by misconfigured DHCP servers.
SolarWinds IP Tracker is only supported by Windows systems.
Price:
100% Free.
Download:
Register in SolarWinds to download the software for free.
IP Address Management (IPAM)
Basic IP Address Scanning should be enough to manage small networks. But when networks scale they depend on multiple subnets and detailed management requirements. Although SolarWinds IP Tracker is able to find IP address conflicts, it is not able to control them.
Sometimes large-scale networks have standalone DHCP and DNS Servers in order to assign addresses to multiple subnets. But IP conflicts occur and it is really challenging to manage them manually. An IP Address Management or “IPAM” is a piece of software able to actively control DHCP and DNS. It also gives you the ability to manage multiple subnets.
5. SolarWinds IP Address Scanner
Among SolarWinds powerful tools, the IP Address Manager does everything a large-scale enterprise needs to manage its addresses properly. It automates many processes to make IP Address management easier. From automated IP address tracking, quick static IP reservations, to multi-vendor DHCP and DNS support.
SolarWinds IPAM comes with an integrated IP address management, DHCP, and DNS tools to administer your entire network.
One of the most commonly used tools from this bundle is the IP Address Scanner. This tool allows you to create automated IP address scans to maintain an updated inventory of all IP address blocks in the network. This is achieved by sending regular ICMP and SNMP polls. The automatic scans use ICMP polls to gather status of the IP address and hostname information. It also uses SNMP to find information on MAC addresses and other vendor information. SolarWinds IP Address Scanner supports both IPv4 and IPv6 address management.
Mac Scan For Ip Addresses On Network Topology
SolarWinds IPAM also provides detailed reports of your IP address in real-time.
Price:
Scan For Ip Addresses On Network Cmd
Download the Free Trial for 30 Days!
Download:
Scan Ip Addresses On Network Mac Terminal
Get a fully functional SolarWinds IPAM for 30 days by registering to SolarWinds official site.
